The connection between exercise and overall health is established, but one of the most surprising advantages is to the gut. The gut is essential for digestion, immune health, and mental health. Research has shown in recent times that exercise can have a significant influence on gut microbiota, energizing a healthy digestive system and reducing gastrointestinal disorders. Having the science of exercise gut health and digestion knowledge can help one get the most out of one’s fitness training in order to help digestive health.
How Exercise Affects Gut Health
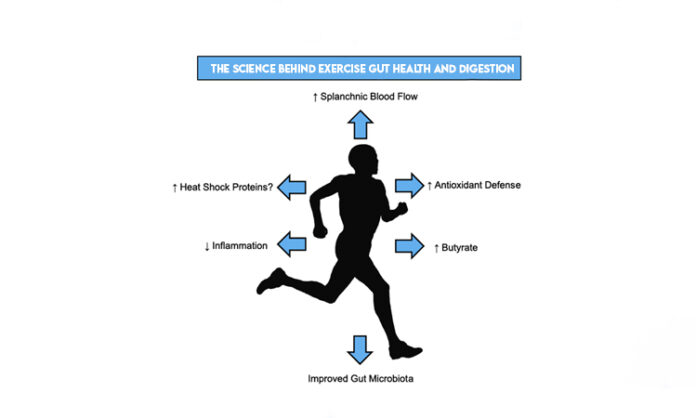
Gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria that help digest food, regulate the immune system, and even influence mood and thought. If the microbiome becomes unbalanced, it can lead to digestive disease, inflammation, and other illness. Fortunately, regular exercise encourages a diverse, rich gut microbiome. This is how exercise influences gut health:
Increases Healthy Bacteria: Studies show that frequent exercisers have higher levels of healthy bacteria, helping with digestion and nutrient absorption.
Reduces Inflammation in the Gut: Exercise is an anti-inflammatory activity and will decrease issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and bloating.
Increases Gut Motility: Exercise gets the digestive system moving, preventing constipation and leading to regular bowel movements.
Balances Gut Microbiota: An active lifestyle encourages diversity of microbes, the secret of healthy gut.
Reduces Stress: Exercise helps lower cortisol, which is instrumental in stress management, a clinically proven gut function inhibitor.
Role of Various Exercises in Gut Health
All exercises are not alike when it comes to gut health. Different types of exercises bring different benefits in terms of digestion and microbial harmony. Let us have a glimpse of some of the best exercise to improve gut health.
Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardio exercises such as running, cycling, and swimming are good for gut health by increasing circulation, reducing inflammation, and stimulating intestinal movement. Regular cardiovascular exercise has been linked to greater gut microbiota diversity, which is crucial for digestion and overall health.
Strength Training
Strength training enhances digestion by reducing visceral fat, which is associated with gut inflammation and metabolic illness. Further, resistance exercises enhance metabolism, which in turn accelerates a healthy gut.
Yoga for a Healthy Gut
Yoga is particularly beneficial for the gut due to the fact that it involves movement, stretching, and controlled breathing. Certain yoga postures stimulate digestion and dispel bloating through massage action on internal organs. Yoga, if practiced on a regular basis, can manage bowel movements and eliminate stress-based gastrointestinal issues.
A few widely known yoga postures that benefit digestion are:
Twisting Poses (such as Seated Spinal Twist): Help cleanse the digestive tract and enhance the uptake of nutrients.
Forward Folds (e.g., Child’s Pose): Decrease bloating and increase gut motility.
Belly Breathing Techniques: Engage the parasympathetic nervous system, decreasing stress and enhancing gut function.
How Movement Aids Gut Health
Physical activity of any kind is beneficial to gut health, but how exactly does movement affect digestion? Knowing how movement aids gut health gives us a better understanding of why being active is so important for a healthy digestive system.
Promotes Blood Circulation: Physical exercise enhances the circulation of blood to the digestive system, making it function optimally.
Triggers Peristalsis: Exercise triggers the rhythmic contractions of the gastrointestinal tract, prevents constipation, and causes healthy bowel movement.
Regulates Hormonal Balance: Hormones play a very crucial role in digestion. Exercise maintains hormonal balance, particularly those that deal with stress, metabolism, and gut function.
Improves Nutrient Absorption: Exercise increases oxygen supply to the digestive system, facilitating food breakdown and nutrient absorption.
Ideal Exercise Routine for Gut Health
A right mix of exercises in your fitness regimen can optimize digestion and improve overall gut health. Here’s a scheduled weekly routine to follow:
Monday: Cardio & Activation of Core
30-minute jogging or brisk walk
3 sets of planks (30-60 seconds per hold)
15 bicycle crunches (3 sets)
Tuesday: Strength Training
Squats (3 sets of 12 reps)
Deadlifts (3 sets of 10 reps)
Push-ups (3 sets of 15 reps)
Wednesday: Yoga for a Healthy Gut
15 minutes of twisting poses and belly breathing techniques
10 minutes of seated forward folds and relaxation poses
Thursday: Low-Impact Movement
30-minute walk
10 minutes of gentle stretching
Friday: Cardio & Resistance Training
20 minutes of cycling or running
3 sets of lunges (12 reps per leg)
Saturday: Active Recovery (Yoga & Mobility Work)
20 minutes of yoga with gut-soothing poses
10 minutes of breathing work to promote relaxation
Sunday: Rest & Relaxation
Gentle stretching or short walk
Mindful hydration and eating
Maximizing the Gut-Improving Benefits of Exercise Tips
In order to achieve maximum benefits for the gut due to exercise, adopt the following habits of daily life:
Hydrate Yourself: Water facilitates digestion and helps in avoiding constipation.
Eat a High-Fiber Diet: Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains encourage a healthy gut microbiome.
Avoid Overtraining: Excessive exercise can stress the body and destroy gut health.
Practice Mindful Eating: Eating slowly and chewing well facilitate digestion.
Manage Stress: Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to reduce stress-related gut issues.
Conclusion
The connection between exercise gut health and digestion is unquestionable. Regular exercise not only makes muscles strong and increases energy but also helps to create a healthy gut microbiome. Whether it’s cardio, strength training, or yoga for a healthy gut, regular exercise leads to improved digestion, less inflammation, and overall well-being. Knowing how exercise helps the gut helps people take control of their digestive health and maximize their fitness programs for long-term health. By integrating exercise with conscious eating and stress management, a healthy and balanced gut is